Governance Operation
Corporate Governance Evaluation Results
| Corporate Governance Evaluation | Number of Listed Companies | Number of OTC Companies | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Listed Companies | Good Way Ranking Range | Number of Listed Companies | Good Way Ranking Range | |
| 2024 (11th) | 778 | 51% - 65% | 802 | 41% - 60% |
| 2023 (10th) | 754 | 51% - 65% | 816 | 41% - 60% |
| 2022 (9th) | 734 | 51% - 65% | Not disclosed | |
| 2021 (8th) | 726 | 51% - 65% | Not disclosed | |
| 2020 (7th) | 712 | 36% - 50% | Not disclosed | |
| 2019 (6th) | 699 | 21% - 35% | Not disclosed | |
| 2018 (5th) | 686 | 21% - 35% | Not disclosed | |
| 2017 (4th) | 675 | 21% - 35% | Not disclosed | |
| 2016 (3rd) | 653 | 21% - 35% | Not disclosed | |
Integrity Management
Directors, managers, employees, appointed representatives, and ultimate controlling persons of the Company are required to exercise the due care of a prudent administrator, diligently supervise the prevention of unethical behavior, and continuously review and improve the implementation effectiveness to ensure the full execution of the integrity management policy.
To strengthen integrity management, the Company has designated the Office of the Chairman as the responsible unit under the Board of Directors. This unit is in charge of formulating integrity policies and preventive measures and supervising their implementation.
Main Responsibilities
- Integrating integrity and ethical values into corporate business strategies and establishing anti-corruption and anti-fraud measures in compliance with laws and regulations.
- Developing preventive programs against unethical behavior and establishing relevant standard operating procedures and codes of conduct.
- Planning internal organizational structures, functions, and segregation of duties, and implementing mutual supervision mechanisms for business activities with higher integrity risks.
- Promoting and coordinating integrity policy education and training.
- Establishing whistleblowing mechanisms and ensuring their effective operation.
- Assisting the Board of Directors and management in reviewing and evaluating the effectiveness of integrity-related preventive measures and issuing periodic compliance reports.
Whistleblowing Mechanism
The Company established the “Code of Integrity Management” and a whistleblowing system in 2013. Relevant reporting channels, procedures, and response mechanisms are disclosed on the Company’s official website.
To ensure sustainable development and encourage the reporting of illegal conduct, the Company clearly stipulates in its Corporate Social Responsibility Code of Conduct that whistleblowers’ identities will be kept confidential, including anonymous reporting, to safeguard the privacy of both suppliers and employees.
Implementation of Integrity Management
The Company conducts at least one internal integrity promotion program annually for all directors, managers, and employees. Training is carried out through courses, email announcements, and written circulation to reinforce the integrity management policy and proactively prevent unethical behavior.
To date, no incidents of unethical conduct have occurred within the Company, and the actual implementation remains fully consistent with the Company’s code.
The Company reports the implementation status to the Board of Directors on a regular basis (at least once per year).
The most recent report was submitted on November 4, 2025.
Status of Reports Submitted to the Board of Directors 2025
In 2025, the Company conducted integrity-related education and training programs with a total of 1,654 participant attendances.
Promotion of the Code of Integrity Management
Risk Management
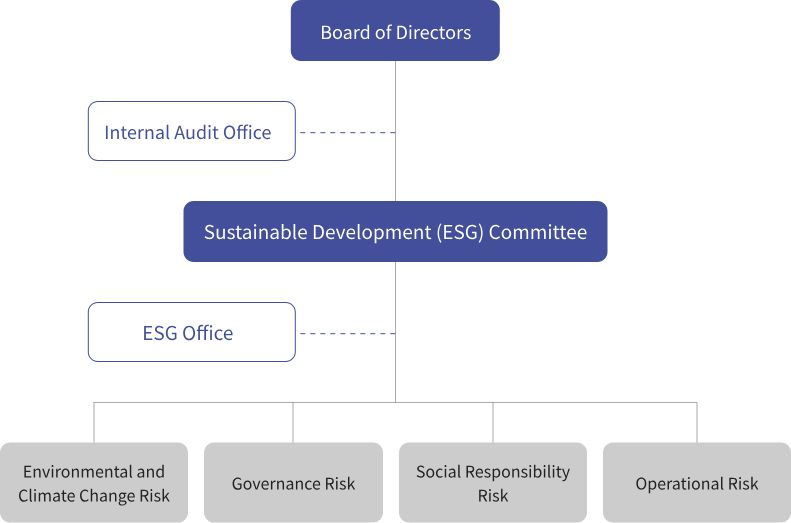
To enhance corporate governance and mitigate various risks that may arise during operations, Good Way has established a “Corporate Risk Management Policy and Procedures.” We follow the principle of materiality to identify, evaluate, address/monitor, and report/disclose risks and opportunities related to environmental, social responsibility, and corporate governance issues. Good Way has developed risk management strategies and designated responsible units for various potential risks. This includes direct risk management units (operational units/first layer of control), risk management and control units (second layer of control), and the Internal Audit Office (third layer of control). Comprehensive risk management is conducted from direct units to control units. Additionally, the operation of risk management is reported annually by the Risk Management Representative to the Sustainability Development Committee and the Board of Directors at least once a year.
Good Way Risk Governance Structure
Information Security Governance
Information Security Management Strategy and Framework
Information Security Policy
To ensure the safety and stability of Good Way’s network and information usage environment, Good Way has established the “Information Security Risk Management Procedures” in accordance with the “Guidelines for Cybersecurity Management of Listed Companies” issued by the regulatory authority.
The Information Department is responsible for the implementation of information security operations, which includes the identification and risk assessment of core business and information systems, security measures for the development and maintenance of information systems, protective and control measures for information security, management measures for outsourcing information systems or services, incident response and information evaluation for information security incidents, and mechanisms for continuous improvement and performance management of information security.
Specific Information Security Management Plans and countermeasures
| Category | Countermeasures / Actions | |
|---|---|---|
| Network Security | Network Resource Management | 1. Disable unused services and functions on network devices to reduce risks. 2. Establish a network monitoring system to understand network operations in real-time and detect potential risks or network failures early. |
| Network Security Management | 1. Install firewalls at the interface between the internal and external networks to prevent unauthorized access and regularly review firewall rules to ensure appropriate settings. 2. Engage external experts or conduct internal assessments for network system security and perform security patches to enhance defense capabilities. 3. Implement various security measures such as data encryption, identity verification, and electronic signatures for external connection information systems based on data and system importance to reduce risks of intrusion, damage, tampering, deletion, or unauthorized access. | |
| Wireless Network Security | 1. Conduct a thorough security assessment before setting up and using a wireless network. 2. Use encrypted communication protocols between wireless network cards and wireless base stations. | |
| Computer Security | Anti-virus Software | 1. Install antivirus software on all computer systems, implement automatic virus database updates, and perform regular virus scans. |
| Access Security | 1. Assign a unique account to each computer system user with the minimum required permissions for their job. 2. Immediately cancel or adjust account permissions for employees upon resignation or job transfer. 3. Regularly review account and permission status to ensure they reflect current conditions. | |
| Password Security Management | 1. Set unique passwords for all access accounts and require users to change their passwords after the first login, establish and enforce strong password settings, and lock accounts temporarily after three incorrect password attempts. 2. Passwords should not be visibly displayed on computer screens when being entered. 3. Encrypt files containing passwords. | |
| Application System Management | Email Security | 1. Explicitly prohibit employees from using company email for activities unrelated to work and educate employees to avoid opening suspicious emails. 2. Set rules and limitations on email content and size based on business and personal needs. 3. Enable email filtering and antivirus mechanisms to block spam and potentially virus-infected emails. |
| Instant Messaging Software Security | Installation and use of instant messaging software must be carefully assessed based on actual business needs and appropriate security controls must be implemented. | |
| Data Security and Backup | 1. Equip data centers with temperature control devices, fire safety systems, and access control measures, limiting entry to specific personnel, back up databases such as SAP/BPM/PLM daily, and establish an off-site backup mechanism. 2. When decommissioning any data storage media, thoroughly destroy its contents to prevent data recovery. 3. Store and safeguard physical confidential documents such as paper files and important contracts. | |
| Abnormal Event Handling and Disaster Recovery Plan | 1. Develop standard procedures for common information security incidents and abnormal situations to increase processing efficiency and reduce harm. 2. Evaluate and address major business impact threats based on business continuity principles, and develop disaster recovery plans accordingly. | |
| Personnel Security | Personnel Security Management | 1. Clearly define the responsibilities of Good Way’s information department personnel. 2. Require personnel handling information security-related work or confidential information to sign confidentiality agreements. 3. Ensure that at least two people are familiar with various information security tasks to handle emergencies. |
| Security Awareness Training | 1. Immediately inform employees about information security incidents. 2. Provide regular information security awareness or training to employees. | |
| Outsourcing | Outsourcing Management | 1. When outsourcing information services, sign contracts with vendors and include confidentiality clauses. 2. Upon completion of outsourced computer system services, request detailed system files and manuals from the vendor. 3. Appropriately control system usage permissions for outsourced personnel stationed at Good Way. |
Resources Invested in Information Security and Status
Good Way installs real-time antivirus software on newly purchased computers and activates automatic and periodic virus database updates. To ensure that all information systems can continue to provide stable services, regular vulnerability scans are conducted to identify potential risks and perform vulnerability remediation. Good Way uses Trend Apex One services to establish 24/7 real-time protection against abnormal network traffic, intrusion attacks, and malicious connections, and regularly sends protection reports to monitor the effectiveness of security measures. The Information Department continuously publishes information security awareness articles within the group to enhance employees’ information security knowledge, aiming to maintain a record of no information security incidents. To ensure that Good Way maintains a record of no information security incidents resulting in data loss, temperature control and fire safety systems have been installed in the data center, access control has been implemented, and critical databases such as SAP/BPM/PLM are backed up daily with an off-site backup mechanism, with backup data retained for 30 days.
Good Way has always emphasized information security-related operations to maintain the confidentiality, integrity, availability, and legality of company information. Good Way is committed to avoiding situations where information and assets are improperly used, disclosed, altered, damaged, or lost due to human error, deliberate destruction, or natural disasters. Good Way’s information system hardware infrastructure and protective facilities have been enhanced to improve the ability to respond to information security incidents, protecting Good Way’s and customers’ assets. The Information Department regularly performs various information security-related tests and assessments each year.
In accordance with our "Information Security Management Procedures", social engineering drills were conducted on 2024/09/30, 2024/10/2, and 2024/10/4. We also conducted information security education and promotion for our staff on 2024/12/3, 2024/12/4, 2024/12/5, and 2024/12/10.
